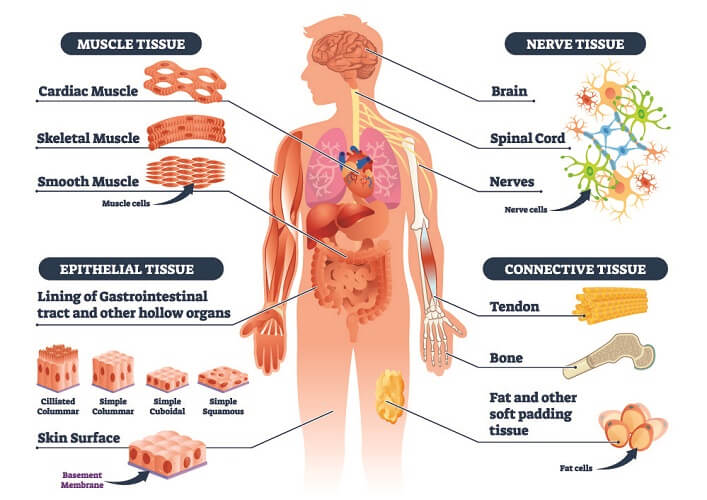
As the name suggests, connective tissue serves an associating capability: it supports and ties different tissues in the body. Not at all like epithelial tissue, which comprises cells that are firmly stuffed together, connective tissue commonly comprises cells dispersed all through an extracellular lattice of sinewy proteins and glycoproteins joined to a storm cellar layer. The essential components of connective tissue incorporate a ground substance, filaments, and cells.
Find some more information here
There are three fundamental gatherings of connective tissues:
Free connective tissue holds organs set up and interfaces epithelial tissue to other fundamental tissues.
Thick connective tissue assists with associating muscles with endlessly unresolved issues.
Particular connective tissue envelops a wide range of tissues with specific cells and remarkable ground substances. Some are strong and solid, while others are fluid and adaptable. Models incorporate fat, ligament, bone, blood, and lymph.
The ground substance goes about as a liquid lattice that suspends cells and strands inside specific connective tissue types. Connective tissue filaments and grids are blended by particular cells called fibroblasts. There are three fundamental gatherings of connective tissues: free connective tissue, thick connective tissue, and concentrated connective tissue.
Free connective tissue
In vertebrates, the most widely recognized sort of connective tissue is free connective tissue. It holds organs set up and associates epithelial tissue with other hidden issues. Free connective tissue is so named in view of the kind of “weave” and its constituent filaments. These strands structure a sporadic organization with spaces between the filaments. The spaces are loaded up with ground matter. The three fundamental kinds of free connective strands incorporate collagenous, flexible, and reticular filaments.
Collagenous filaments are made of collagen and comprise heaps of strands that are curls of collagen particles. These strands assist with fortifying the connective tissue.
Flexible strands are made of the protein elastin and are stretchable. They assist with giving the connective tissue flexibility.
Find some more information about the Poland flag
Reticular strands associate connective tissues with different tissues.
Free connective tissue offers the help, adaptability, and strength expected to help interior organs and designs like veins, lymphatic vessels, and nerves.
Thick connective tissue
One more sort of connective tissue is thick or sinewy connective tissue, which can be tracked down in ligaments and tendons. These designs help to interface muscles to endlessly unresolved issues. Thick connective tissue is made out of countless firmly stuffed collagenous filaments. Contrasted with free connective tissue, thick tissue has a higher proportion of collagenous strands to ground matter. It is thicker and more grounded than free connective tissue and structures a defensive case layer around organs like the liver and kidneys.
Thick connective tissue can be arranged into thick ordinary, thick unpredictable, and flexible connective tissues.
Thick Regular: Tendons and tendons are instances of thick standard connective tissue.
Thick sporadic: Most of the dermis layer of the skin is comprised of thick unpredictable connective tissue. The film case encompassing numerous organs is likewise a thick sporadic tissue.
Flexible: These tissues empower extending of designs like the veins, vocal ropes, windpipe, and bronchial cylinders in the lungs.
Explicit connective tissue
Particular connective tissues incorporate various tissues with specific cells and exceptional ground substances. A portion of these tissues is strong and solid, while others are liquid and adaptable. Models incorporate fat, ligament, bone, blood, and lymph.
Fat tissue
Fat tissue is a type of free connective tissue that stores fat. Fat lines mark organs and body cavities to shield organs and safeguard the body from heat misfortune. Fat tissue additionally delivers endocrine chemicals that influence exercises, for example, blood thickening, insulin awareness, and fat stockpiling.
The essential cells of fat are adipocytes. These cells store fat as fatty oils. Adipocytes show up around and enlarged when fat is stored and shrivel as fat is spent. The greater part of the fat tissue is depicted as white fat which stores energy. Both brown and beige fats consume fat and produce heat.
Ligament
The ligament is a type of sinewy connective tissue made out of collagenous strands firmly stuffed in a rubbery coagulated substance called chondrin. The skeletons of sharks and human undeveloped organisms are made of ligament. Ligament offers adaptable help for specific designs, including the nose, windpipe, and ear, in grown-up people.
There are three unique kinds of ligaments, each with various qualities.
Hyalin ligament is the most well-known type and is tracked down in regions like the windpipe, ribs, and nose. The hyaline ligament is adaptable, flexible, and encircled by a thick film called a perihelion. ondrium.
Fibrocartilage is the most grounded kind of ligament and is made out of hyaline and collagen thick strands. It is firm, extreme, and situated in regions, for example, between vertebrae, in certain joints, and in heart valves. Fibrocartilage doesn’t have perichondrium.
Versatile ligament contains versatile strands and is the most adaptable sort of ligament. It is tracked down in areas like the ear and larynx (voice box).
Bone Tissue
Bone is a sort of mineralized connective tissue that contains collagen and calcium phosphate, a mineral gem. Calcium phosphate gives bone immovability. There are two sorts of bone tissue: supple and reduced.
Springy bone, likewise called cancellous bone, gets its name on account of its elastic appearance. The enormous spaces, or vascular holes, in this kind of bone tissue contain veins and bone marrow. Elastic bone is the primary bone sort framed during bone development and is encircled by smaller bone.
Smaller bone, or cortical bone, areas of strength for and frames the hard external bone surface. Little waterways inside the tissue consider the section of veins and nerves. Mature bone cells, or osteocytes, are seen in minimal bone.
Blood and Lymph
Sufficiently intriguing, blood is viewed as a kind of connective tissue. Like other connective tissue types, blood is gotten from the mesoderm, the center microbe layer of creating undeveloped organisms. Blood likewise interfaces other organ frameworks together by providing them with supplements and moving sign atoms between cells. Plasma is the extracellular lattice of blood with red platelets, white platelets, and platelets suspended in the plasma.
Lymph is one more sort of liquid connective tissue. This reasonable liquid starts from blood plasma that ways out veins at hairlike beds. A part of the lymphatic framework, lymph contains safe framework cells that safeguard the body against microorganisms. Lymph is conveyed back to blood dissemination through lymphatic vessels.